VR Surgical Training Enhancing Precision and Reducing Errors in the OR
Virtual reality (VR) technologies have evolved very fast in recent years. The technology's most prevalent use aside from gaming, is in education.
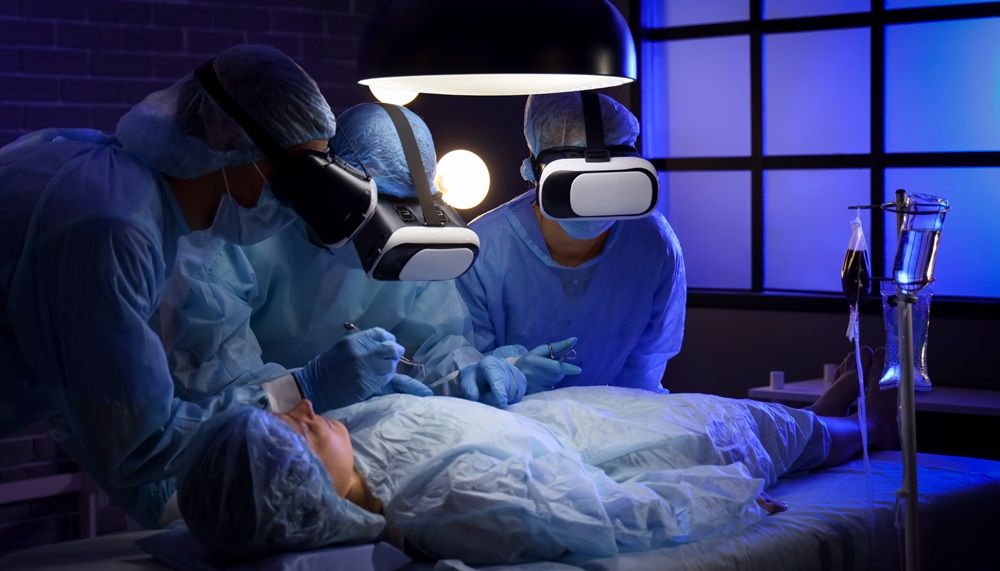
In the healthcare sector, VR technologies have been used in various areas. It has ushered in a new world of medical training, especially in surgery.
VR training allows surgeons to improve their skills, increase patient safety, and decrease errors before entering a real operating room. Surgical pathways and the training of surgical skills can be investigated safely and cost-effectively using AR/VR medical training.
This article addresses the application of VR surgical training and 3D reconstruction of internal organs and feasible surgical pathways.
The Effect of VR Surgical Training on Contemporary Healthcare
In the guise of virtual reality (VR), it is amazing how technology is finding unimaginable applications such as critical healthcare, becoming a core component of training healthcare professionals, improving medical procedures, and developing VR and AI patient care apps.
Surgical mistakes are irreversible, and conventional training fails to equip surgeons with the necessary skills to cope with high-pressure situations. Training in VR-powered virtual and safe enviorment bridges this gap by allowing learners to engage in realistic simulations replicating real situations.
Benefits of VR Surgical Training
- Hands-on Learning in a Controlled Environment
- Improved Surgical Planning and Visualization
- Error Reduction and Increased Precision
- Cost-Effective Training
Impact of Immersive Training Integration into Surgical Practice
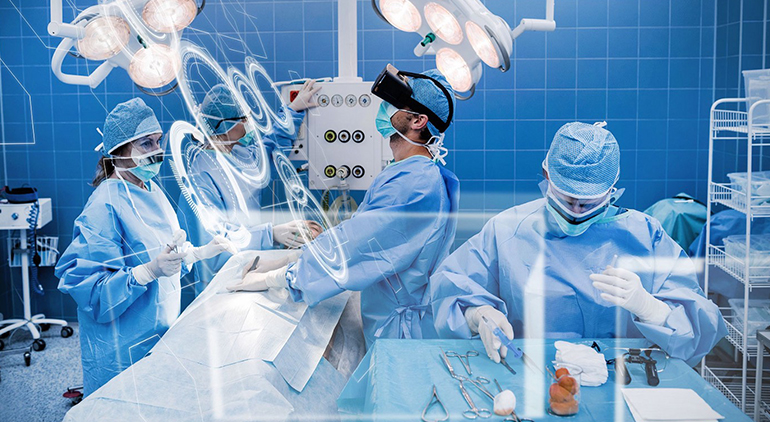
AR/VR in healthcare has advanced various aspects of surgical practice, including intraoperative guidance, preoperative planning, and postoperative training.
1. Preoperative Planning
AR and VR introduce new methods to study three-dimensional anatomical structures for preoperative planning.
Although AR allows digital data to be projected onto the patient pre- and perioperatively, VR enables the surgeon to study the anatomical complexity in a virtual environment.
Therefore, including augmented and virtual reality in surgery and preoperative planning is beneficial regarding operative time, technical accuracy, complications, and overall intervention expenses.
2. Intraoperative Guidance
One of the greatest benefits of augmented reality in surgery is that it allows doctors to visualize inside images right away without looking away from the screen to view digital scans.
AR can also help surgeons navigate difficult anatomical routes.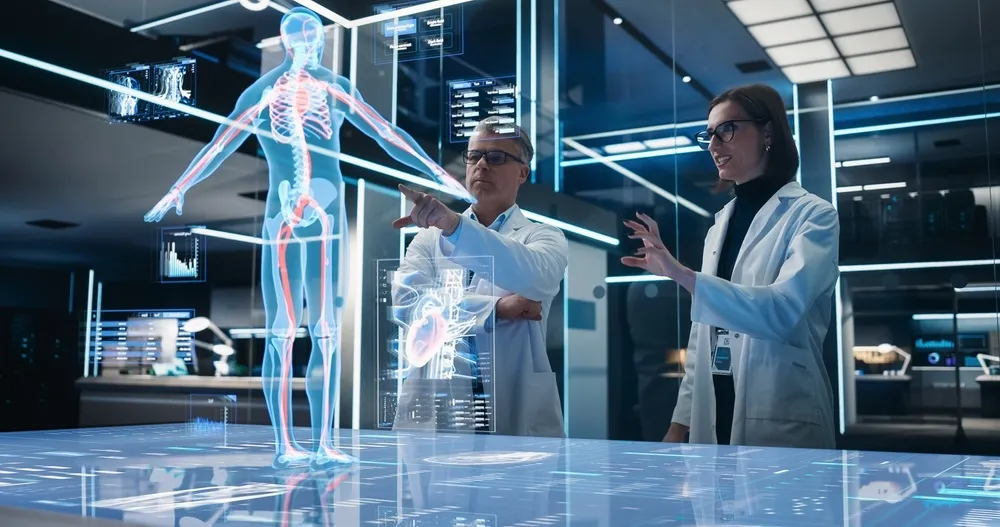 For instance, it can superimpose a patient's internal anatomy over the surgeon's line of sight and allow for accurate incisions and reduced trauma to the surrounding tissue.
For instance, it can superimpose a patient's internal anatomy over the surgeon's line of sight and allow for accurate incisions and reduced trauma to the surrounding tissue.
3. Increased Visualization
AR and VR both aid in three-dimensional visualization of anatomical structures. This sense of depth increases the surgeon's sense of spatial relationships and makes procedures more precise.
Surgeons can see such important organs like blood vessels and nerves in high resolution, hence becoming safer against accidental damage. Planning and surgical visualization contribute greatly towards decreasing accidents in the healthcare industry.
Boost surgical precision & cut errors with VR training. Train smarter, operate safer!
See VR in Action4. Linking Remote Clinical Teams
VR and AR facilitate remote collaboration among surgeons, enabling them to exchange ideas and consult on cases in real time. This works especially well for training, knowledge exchange, and expert advice.
This alleviated the demand for surgical personal protective equipment, which was low in supply because of COVID-19, and facilitated remote doctors to consult and work together. It also reduced face-to-face exposure.
5. Education and Training
More than 5 billion individuals worldwide do not have access to safe surgery due in large part to a lack of educated surgeons. AR in healthcare education has provided the ability to learn in a secure and accessible environment, causing a great influence on countries where access to contemporary surgical training is low.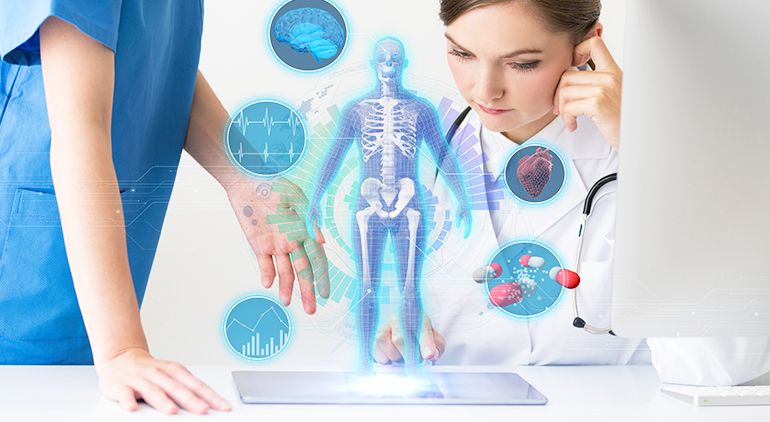 Surgeons and medical students can engage fully in AI in healthcare. They can keep practicing surgery on computer patients, erasing blunders and recovering from them, without putting real patients at risk.
Surgeons and medical students can engage fully in AI in healthcare. They can keep practicing surgery on computer patients, erasing blunders and recovering from them, without putting real patients at risk.
6. AR/VR for Dental Surgeries
To our surprise, AR/VR has been mainly used in dentistry, particularly dental implantology and orthognathic surgery. Virtual planning is advantageous in dental implants, improving accuracy if dynamic navigation or statistical guiding is employed.
VR has also been employed to facilitate oral and maxillofacial surgery education and training. It enables students to train procedures without working on real patients by replicating surgical conditions.
7. Reduced Radiation Exposure
Treatments that would otherwise be necessitated by fluoroscopy or other forms of radiation-based imaging methods are now achievable without radiation due to AR technology.
Surgeons may employ AR image guidance to reduce repeated ionizing radiation exposure required during minimally invasive surgery. This benefits the patient and healthcare providers alike by reducing exposure to health hazards resulting from diminished exposure to radiation.
Augmented and Virtual Reality in Surgery: Crossing Barriers towards Improving Healthcare
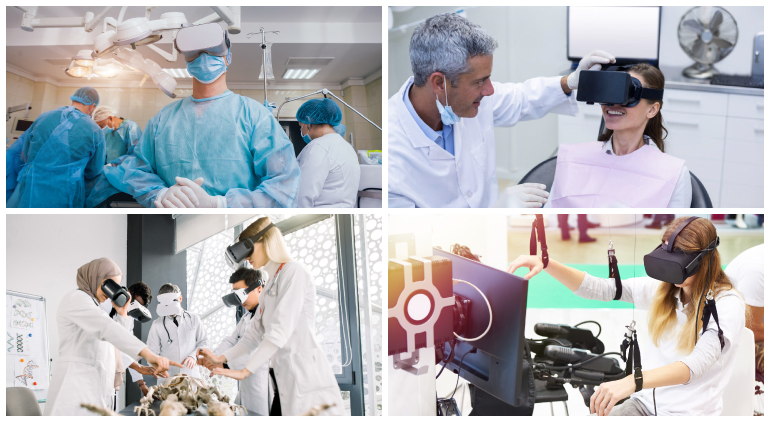 Augmented and virtual reality are transforming surgical procedures, enhancing precision, and improving patient outcomes. However, several challenges must be addressed, including:
Augmented and virtual reality are transforming surgical procedures, enhancing precision, and improving patient outcomes. However, several challenges must be addressed, including:
1. Technical Complexity
Implementing AR/VR development solutions in surgery demands advanced technical infrastructure and compatibility, and it is challenging to integrate the systems with no loss of functionality.
The difficulty is in devising a harmonized and coherent environment in which AR/VR interacts with the available infrastructure smoothly without creating disturbances or impacting the efficiency of surgical interventions.
2. Cost Implications
The initial investment required to adopt AR/VR technology in healthcare is prohibitive and viewing long-term value is important for its adoption on a large scale.
Adopting VR and AR technology comes with the tendency to require an enormous amount of initial investment, mainly the price of software, maintenance, and hardware.
3. Data Privacy and Security Issues
AR/VR deployment in surgery poses data protection problems, including patient confidentiality protection, encryption of data in a secure manner, and cyber protection.
There is a need for compliance with healthcare regulations, proper authentication controls, and clarity of data ownership and consent. Monitoring and auditing AR/VR systems continuously means that security vulnerabilities are quickly identified and closed.
Enhance surgical precision, reduce errors, and train with confidence using VR-powered simulations.
See VR in Action4. Regulatory Challenges
The regulatory framework for immersive surgery training is changing, and it is hard to keep abreast of norms and legislation to maintain compliance for an easy integration.
For instance, the FDA underlines the necessity of regulation to make sure that the security and effectiveness of AR/VR technology are maintained in healthcare.
5. User Acceptance and Training
A research in the "International Journal of Surgery" found that the overall surgical residents had a positive attitude toward virtual reality in surgery but required training to overcome adversity.
As a result, doctors and surgeons must be trained to implement AR/VR technology properly, and opinions concerning this can be different.
The Future of Augmented and Virtual Reality in Surgical Training & Accuracy
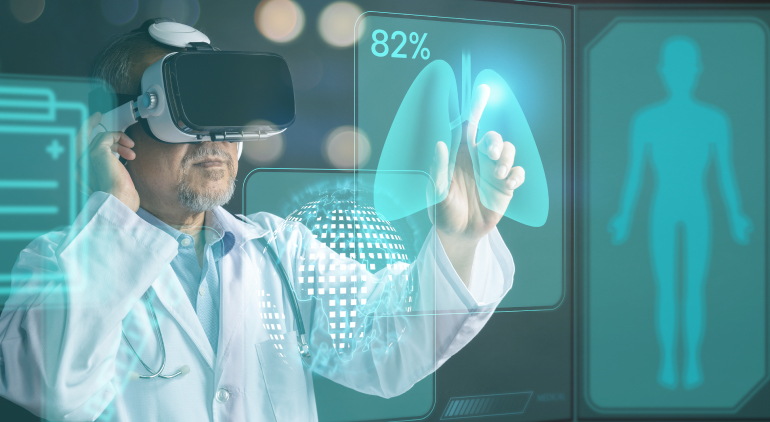

From personalized simulations to virtual consultations and beyond, AR/VR technologies are increasingly being incorporated into the surgeon's toolkit.
The future will be more of a union between AI, AR/VR, and patient-centric care to transform the practice of contemporary medicine, offering an age where precision surgery and empathy meet.
Microsoft's HoloLens is an example of holographic visualization that provides interactive 3D holograms to improve spatial awareness during procedures.
The advancements such as AI in telemedicine and AR in pharma technologies have the potential to bring a new era of fun in surgical medicine, with technology being used to improve patient outcomes, increase applications, and enhance skills.
As a leading AR/VR development company, we offers premium services that allow healthcare professionals to deliver next-generation and collaborative treatment and surgery programs beyond the limits of traditional healthcare systems.
Our experts dedicate themselves to delivering an enhanced user experience with excellent scalability and customization to ensure the development of immersive healthcare platforms for improving patient care and outcomes.







